Azure Databases: Setting up .bash & .pgpass files in RIS server & commands to naviagate:
Most the steps outlined in this document are reference in the ris-etl-deployments repo.
The steps to set up the user's home environment i.e., bash_profile file are outlined in step 5 of the document.
Step 1: Log into the ris server.
ssh -l alvinn compute1-client-2.ris.wustl.edu Step 2: Set up bash_profile & .pgpass profile:
If you do not have a bash file already set up, you can use the following commands to create the .pgpass file & bash_profil:
touch ~/.ssh/.pgpass chmod 600 ~/.ssh/.pgpass # copy pgpass template info echo "# host:port:database:username:password" >> ~/.ssh/.pgpass # This creates the bash_profile cat bash_profile >> ~/.bash_profile Step 3: Set up bashrc file.
If you cureentyl have an existing bashrc file, ensure that all of its content is similar to that ris-etl-deployments-bashrc repo.
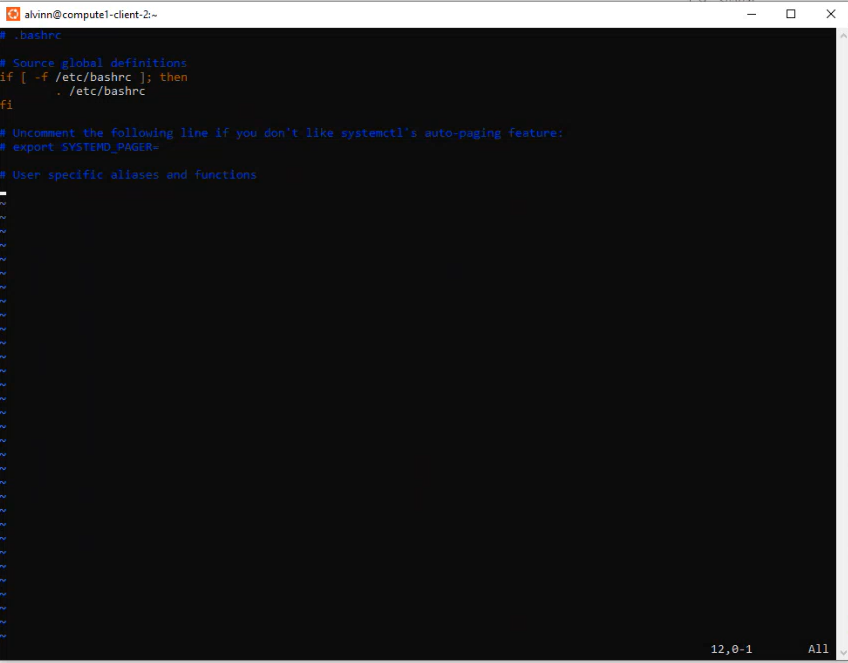
The deleted content of the bashrc file should look like this.
Bashrc pre-edit
(enlarged image)
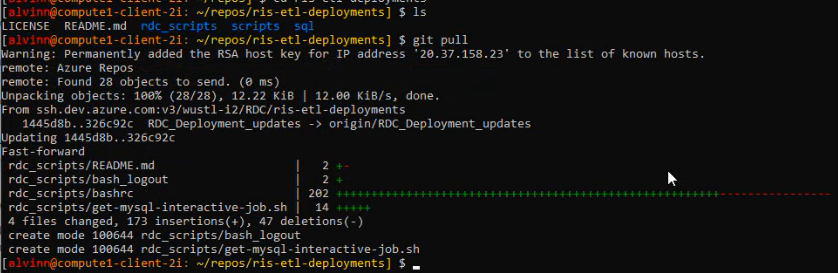
On the ris server, run the following commands:
## Change directory cd /repos/ris-etl-deployments/rdc_scripts # ensure the pull is done in the **RDC_Deployment_updates** branch and not main branch git branch # if not in right branch run the following command checkout branch git checkout RDC_Deployment_updates ## do a git pull git pull
Updating bashrc file
(enlarged image)
Step 5: append the Bashrc file
In the step, we will append te bashrc file from the repo to our local bashrc file.
Run the following commands to achieve this:
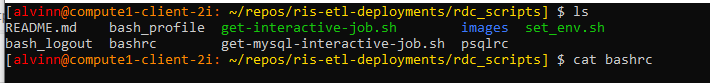
# verify all files in home directory ls -al # go the rdc_scripts cd /repos/ris-etl-deployments/rdc_scripts # view content of bashrc file # to exit the cat view, press q key. cat bashrc # to append bashrc from repo to local bashrc cat bashrc >> ~/.bashrc # view content of new bashrc file less ~/.bashrc
bashrc content
(enlarged image)
Step 7: Validate everything works:
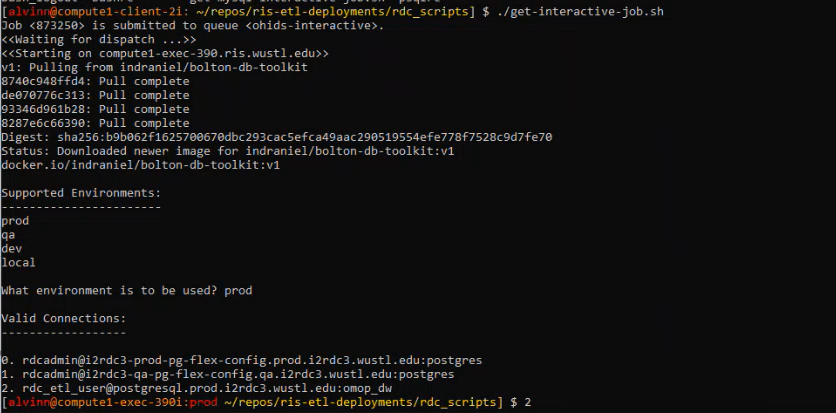
Run the LSAB job to validate:
LSAB job validation
(enlarged image)
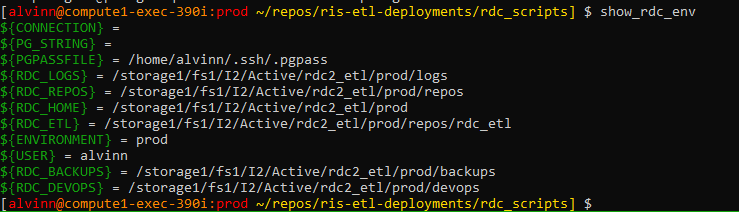
Step 8: verify environment variables:
After selecting the environment, the following command allows you to see the environment variables:
# allows you to view all environment variables after defining your environment show_rdc_env
Validate environment variables
(enlarged image)
Note that each variable points to a specific directory in the repo.
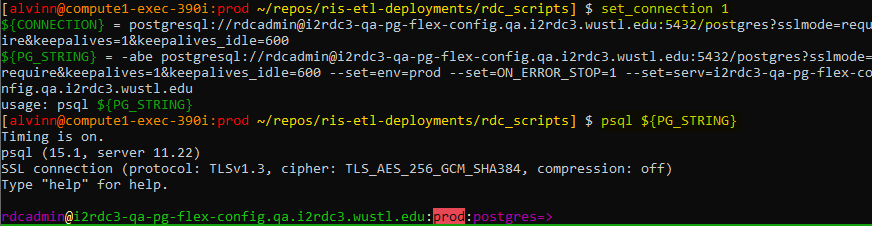
Additionally, note that the {CONNECTION} &
# this script allows you to set the connection using the valid connection table list set_connect 1 ## connect to database: psql ${PG_STRING}
Database connection
(enlarged image)
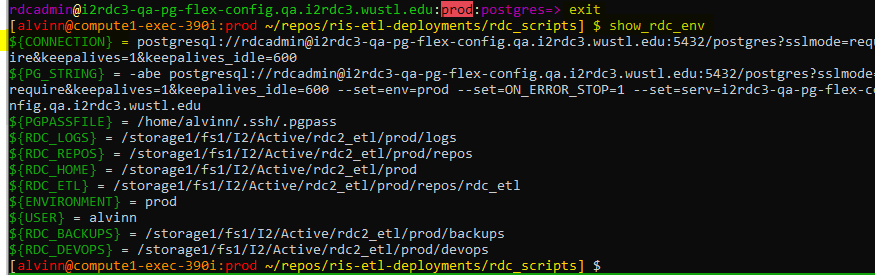
If you exit the database and rerun the show_rdc_env , both of the {CONNECTION} & will be populated.
{CONNECTION} &
{PG_STRING}
(enlarged image)
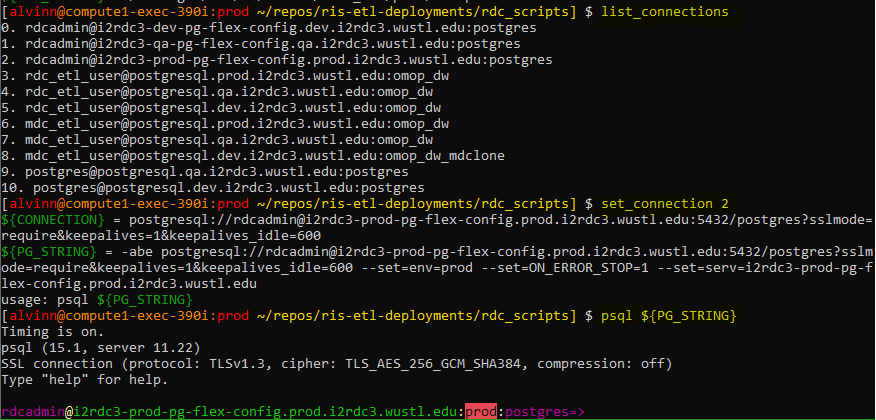
To change to a different database server, run the following command:
# see all databse conections again: list_connections # select connection set_connect 2 ## connect to database: psql ${PG_STRING}
change database connection
(enlarged image)