Getting Started
Laptop/Computer
Software
- DBeaver
- Azure Storage Explorer
- Azure CLI - (if technically minded)
Administrative
Social/Collaboration
Toolings
- Microsoft Outlook - (email)
- Microsoft Teams - (virtual meetings and chat)
- Zoom - (HIPAA/PHI compliant virtual meetings)
- Microsoft Calendar - (group scheduling)
- WUSTL Box - (collaborator file sharing)
- Microsoft One Drive - (internal file sharing)
- Microsoft DevOps: Planning and Administration - (project management tracking)
- Microsoft SharePoint: DataLake Working Group
Microsoft Teams
Meetings
| Day | Time | Length | Frequency | Meeting Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTWThF | 930AM | 15 mins | Daily | TPI Daily Standup |
| MTWThF | 945AM | 15 mins | Daily | Platform Engineering Daily Standup |
| F | 1000AM | 1 hr | Bi-weekly | Platform Engineering Sprint Planning |
| Th | 1230PM | 1 hr | Monthly | I2 Research / Data Services Team Meeting |
| W | 900AM | 1.5 hrs | Monthly | OHIDS Town Hall Meeting |
| W | 330PM | 45 mins | Weekly | Azure Infrastructure Discussion |
Organization
Internal Teams
See I2DB: Centers & Affliated Entities for an overall organizational breakdown. We are a part of Infrastructure Core Services (ICS), a group within the Office of the Chief Research Information Officer.
The ICS group currently consists of 3 main subgroups: Data Brokers, Research Data Core (RDC), and Platform Engineering.
A loose functional description of the groups is:
- Data Brokers are involved with assisting members of the Washington University community with regards to the EHR data managed by ICS group.
- The RDC team is involved with the curation and data engineering of the EHR data collected from the WUSM/BJC ecosystem for research purposes.
- The Platform Engineering team is involved with development, administration and support of the underlying technologies used by the RDC and Data Brokers.
Again, this is a very loose description and division of work; in practice, there's a lot of functional and project overlap amongst the 3 subgroups.
External Teams
The ICS groups also works with a few external teams (with respect to Washington University) for infrastructure and application development.
- Technology Partners -- (infrastructure)
- HICAPPS -- (application development)
Computing
Cloud
RIS
REDCap
JIRA
- https://tpidai.atlassian.net/ -- this is TPI's Jira board for WUSM work
Trainings
Data Lake
Special Projects
Historical Background
Migration to EPIC
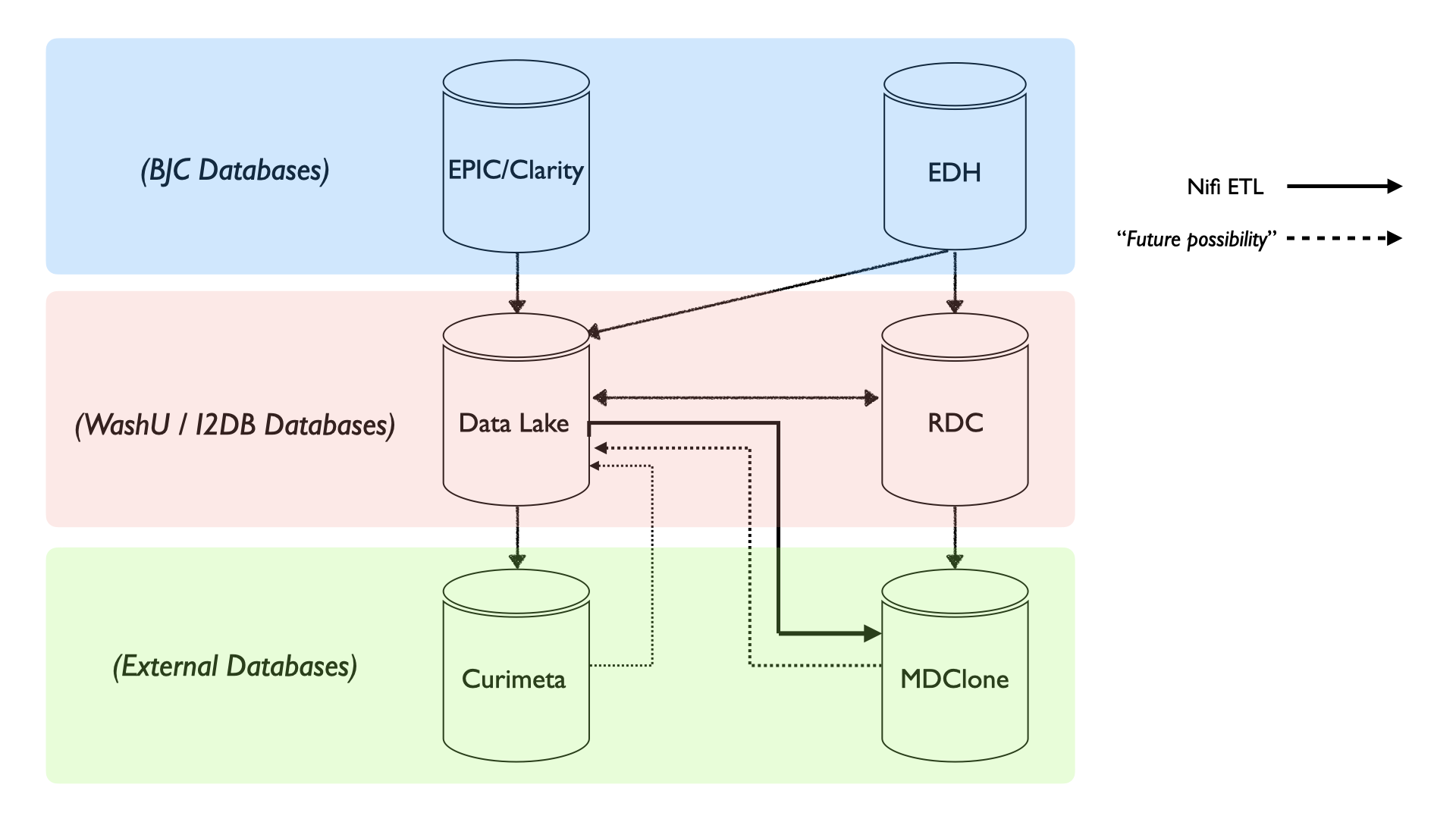
Before 2018 various departments and hospitals across the WashU / BJC ecosystem used their own Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. This made interoperability across the healthcare system inefficient and mistake prone. WashU / BJC systems decided to use EPIC as the main EHR system to resolve these problems. The migration to EPIC across the healthcare system took time, but by June 4, 2018 all hospital and clinics had moved to EPIC/Clarity. Clarity is a nightly incremental backup of the EPIC system.
BJC maintains a clone of the Epic/Clarity system called Enterprise Data Hub (EDH) for data infrastructure purposes.
Only a limited number of users have direct access to the EPIC/Clarity system. Only people with Tier-5 EPIC certifications can directly access the EPIC/Clarity data system.
RDC
The Washington University School of Medicine (WUSM), wants to use the data collected in the EHR system for research purposes. On the WUSM side, via the Institute of Informatics (I2) Data Services group, a daily incremental copy of Clarity, via the EDH, was ingested into a new database called Health Data Coare (HDC). Over time as WashU participated in various data registries, national and local consortiums and research programs, there was a need to transform the EPIC/Clarity data from EDH into a more standardized data schema that would be interoperable for various research needs. This standardized data model is called OMOP. This data translation and transformation of original EPIC/Clarity data, via the EDH, into the OMOP data model is eventually put into a postgres database called the "Research Data Core" (RDC). The direct need to access the HDC has been deprecated.
Data Lake
Additionally, the OMOP data is in parallel placed into the WUSTL Data Lake which is accessed through Databricks, a commercial platform based on the open-source Apache Spark. It's intended to incporate other medical data (e.g. imaging, genetic sequencing, etc.) into the data lake to provide a comprehensive data repository for the WashU research ecosystem.
Data Transformation and Translation or Extract-Transform-Loading (ETL) History
2018-19 (Pentaho data integration)
ETLs mostly happened via various customized SQL scripts and other supporting scripts.
2019-20 (1904 Labs)
The ETL processes were developed by an external vendor, 1904 Labs. They were involved in the initial data migration to the OMOP model. THey used a batching system consisting of various Python and SQL scripts to place data into a staging table, and eventually into an early version of the RDC OMOP schema.
2020-today (TPI)
A new external vendor, Technology Partners, took over the ETL systems from 2020. They moved the 1904 Labs work from Python/SQL scripts into a ETL framework using Apache NiFi. Nifi is based on the Java-ecosystem, hence there was a migration of Python code to Java/Scala code. A one-to-one mapping of Python functionality to Java functionality was one of the initial goals.
TPI started developing the Data Lake architecture and system starting 2022. The Data Lake system is still very much a "work in progress" and is considered "new".
Future
External users -- academic, government, commerical, non-privileged -- would like access to the EHR data; however, external users cannot directly access the OMOP data, as much of it is PHI/HIPAA protected. MDClone and CuriMeta are companies that would like to transform the PHI protected data into either appropriate synthetic, or de-"identified"/anonymized data for 3rd party users to access and explore. This is an ongoing development and collaboration with I2.
Data System Overview
A graphical view of the I2DB database architecture (circa Fall 2023).
REDCap
Biostats
Other Notable Points
- financial BJC data doesn't go into the WashU EHR data system.
Glossary / Acronyms
| Term | Full Meaning |
|---|---|
| RDC | Research Data Core (postgres database; predecessor to data lake) |
| EDH | Enterprise Data Hub (an older BJC data service) |
| EHR | Electronic Health Record |
| EPIC | BJC EHR System - https://www.epic.com |
| clarity | nightly backup of the BJC EPIC backend |
| HDC | Health Data Core (old approach; copy of clarity system from BJC to WashU) |
| OMOP | Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership |
| OHDSI | Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics : https://www.ohdsi.org |
| PHI | Private Health Information |
| TPI | Technology Partners (3rd Party external Team) |
| OHIDS | Office of Health Information and Data Science |
| I2DB | Institute for Informatics, Data Science & Biostatistics |
| ICS | Infrastructure Core Services (as subgroup within OHIDS) |
| CGL | Clinical Genomics Laboratory (in the Deptartment of Pathology) |
| DI2 | Digital Intelligence & Innovation (Digital Transformation) |
| CBDS | Center for Biostatistics & Data Science |
| CACI | Center for Applied Clinical Informatics |
| CPHI | Center for Population Health Informatics |
| CTBI | Center for Translational Bioinformatics |
| CADR | Center for Administrative Data Research (now ADCS) |
| ADCS | Administrative Data Core Services |
| WUSM | Washington University School of Medicine |
| HBCD | Health Brain Child Development (project where I2DB is a DCC) |
| DCC | Data Coordinating Center |



